Managing Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol is a waxy substance similar to fat that is found in every cell of the body. While it plays a crucial role in producing hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids essential for digesting fat, it can also pose significant health risks when present in excess.
Understanding cholesterol is vital for effectively managing your health, particularly in relation to heart disease and stroke.
What is Cholesterol?
Produced primarily by the liver, cholesterol is also obtained from certain foods. It travels through the bloodstream in particles known as lipoproteins, which consist of both fat and protein. While cholesterol is necessary for various bodily functions, an imbalance—especially an excess of certain types—can lead to serious health complications.
Types of Cholesterol: HDL vs. LDL
Cholesterol can be categorized into two main types: HDL and LDL. HDL, or high-density lipoprotein, is often referred to as “good” cholesterol. It helps transport other forms of cholesterol away from the arteries and back to the liver, where it can be processed and removed from the body. Higher levels of HDL are generally associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
OIn contrast, LDL, or low-density lipoprotein, is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. Elevated levels of LDL can lead to the buildup of cholesterol in the walls of arteries, creating blockages that increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Understanding the distinction between these two types is essential for managing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health.
Types of Cholesterol: HDL vs. LDL
There are two main types of cholesterol:
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): is known as “good” cholesterol because it helps eliminate other types of cholesterol from the bloodstream. Higher HDL levels are linked to a reduced risk of heart disease.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “bad” cholesterol, LDL can build up in the walls of arteries, leading to blockages. High levels of LDL cholesterol increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
The Importance of Managing Cholesterol Levels
Managing cholesterol levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing serious medical conditions. High cholesterol can lead to a variety of complications, making awareness and proactive management essential for long-term well-being.
When cholesterol levels become elevated, particularly the “bad” LDL cholesterol, the risks to health significantly increase. High cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, narrowing them and making it difficult for blood to flow freely.
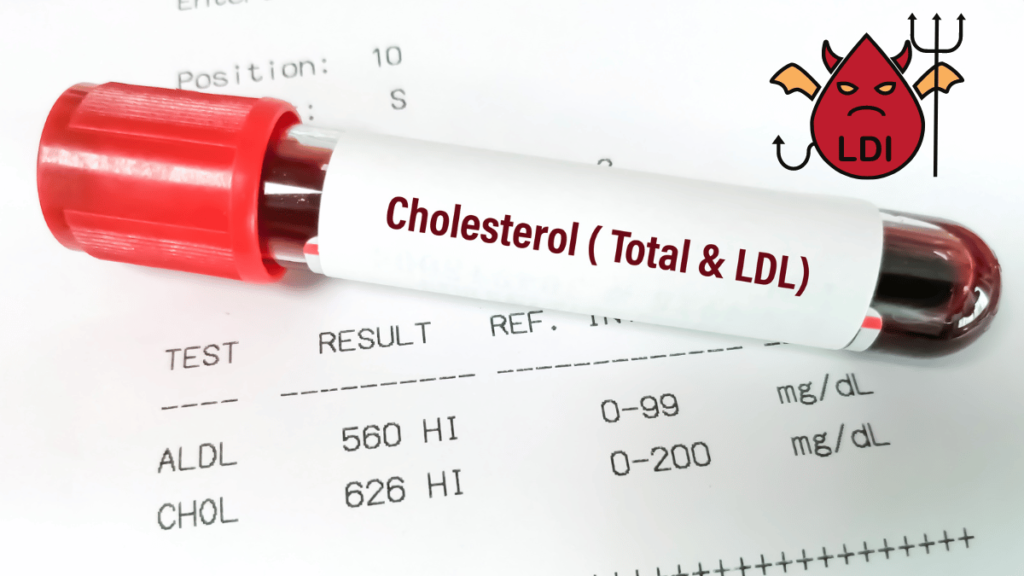
This condition, known as atherosclerosis, can result in serious cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and strokes.
Additionally, high cholesterol is often asymptomatic, meaning individuals may be unaware of their elevated levels until a major health crisis occurs. Therefore, regular monitoring and management are critical to mitigating these risks.
Benefits of Healthy Cholesterol Levels
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels offers numerous benefits for both heart health and overall wellness. When LDL cholesterol is kept in check, and HDL cholesterol levels are elevated, the risk of heart disease and stroke significantly decreases.
Healthy cholesterol levels contribute to better blood circulation and can reduce inflammation within the body. Furthermore, achieving optimal cholesterol levels can enhance energy levels and promote a sense of well-being, allowing individuals to lead a more active and fulfilling life.
Ultimately, effective cholesterol management is a key component of a healthy lifestyle.
Dietary Changes for Managing Cholesterol Levels
Making informed dietary choices is one of the most effective ways to manage cholesterol levels. The foods you consume can have a significant impact on your overall cholesterol profile, influencing both LDL (bad) and HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
Foods to Eat for Lower Cholesterol
Incorporating heart-healthy foods into your diet can help lower cholesterol levels and promote overall cardiovascular health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial.
These healthy fats, found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, can help reduce LDL cholesterol and lower blood pressure. Plant-based sources like walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds also provide omega-3s and can be easily integrated into meals.
Fruits and vegetables are essential components of a cholesterol-lowering diet. They are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help combat inflammation and support heart health.
Berries, citrus fruits, apples, and leafy greens are particularly high in fiber and phytonutrients, making them excellent choices.
Whole grains should be a staple in your diet as well. Foods such as oats, barley, quinoa, and brown rice contain soluble fiber, which binds cholesterol in the digestive system and helps prevent its absorption into the bloodstream. Incorporating beans and legumes—such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans—can further enhance your fiber intake while providing protein and other vital nutrients.
Nuts and seeds are also beneficial for cholesterol management. Almonds, pistachios, and sunflower seeds are rich in healthy fats and can help improve your lipid profile when consumed in moderation.
Foods to Avoid

To effectively manage cholesterol levels, it’s important to limit or avoid certain foods that can elevate LDL cholesterol and negatively impact heart health. Saturated fats, commonly found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and many processed foods, can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
This includes fatty cuts of meat, butter, cream, and cheese. It’s advisable to opt for lean protein sources, such as chicken, turkey, and plant-based proteins like tofu and legumes.
Trans fats are particularly harmful and should be avoided entirely. These fats are often found in fried foods, baked goods, and many commercially prepared snacks.
They not only raise LDL cholesterol but also lower HDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease. Always check food labels for “partially hydrogenated oils,” a common source of trans fats.
Additionally, excessive sugar and refined carbohydrates can contribute to weight gain and elevated cholesterol levels.
Foods high in added sugars, such as sugary beverages, candies, and pastries, can lead to increased triglyceride levels. Instead, focus on whole foods and complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
The Role of Fiber in Cholesterol Management
Fiber is a crucial component of a heart-healthy diet, especially soluble fiber, which plays a significant role in cholesterol management. Soluble fiber can help lower LDL cholesterol by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
This type of fiber is found in various foods, including oats, barley, beans, lentils, apples, and citrus fruits.
Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your meals can not only help manage cholesterol levels but also support digestive health and promote a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management. Aim to include sources of both soluble and insoluble fiber in your diet for maximum benefits.
The general recommendation is to consume at least 25 grams of fiber per day for women and 38 grams for men, though individual needs may vary.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Cholesterol Levels
In addition to dietary adjustments, making specific lifestyle changes can significantly impact your cholesterol levels and overall heart health. Adopting healthier habits can lead to lasting improvements and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
The Impact of Exercise
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to improve your cholesterol levels. Engaging in aerobic exercise can help raise HDL (good) cholesterol while lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides. Activities such as brisk walking, running, swimming, cycling, and dancing can be beneficial.
The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous activity. Incorporating strength training exercises at least twice a week can also enhance your metabolic rate and contribute to better cholesterol management.
Even simple changes, like taking the stairs instead of the elevator or going for a walk during lunch breaks, can have a positive impact on your physical activity levels.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight

Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing cholesterol levels effectively. Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can contribute to higher LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol levels.
Carrying excess weight can also lead to insulin resistance and increased triglycerides, further elevating the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Even modest weight loss—typically 5-10% of your total body weight—can significantly improve your cholesterol profile and overall heart health.
Combining a balanced diet with regular exercise is the most effective way to achieve sustainable weight loss. Consider setting realistic goals and seeking support from healthcare professionals or weight management programs if needed.
Reducing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can negatively impact cholesterol levels and overall heart health. Stress may lead to unhealthy behaviors, such as emotional eating, increased alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle, all of which can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels.
Implementing stress-reduction techniques can help mitigate these effects. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep-breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can promote relaxation and improve your overall well-being.
Establishing a routine that includes time for hobbies, social activities, and self-care can also play a crucial role in managing stress and supporting heart health.
Natural Remedies for Managing Cholesterol Levels
In addition to dietary and lifestyle changes, some natural remedies may help in managing cholesterol levels effectively. These approaches can complement traditional methods and provide additional support for heart health.
Supplements to Consider
Certain dietary supplements can support cholesterol management. Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, have been shown to lower triglyceride levels and improve heart health.
If you don’t consume enough fatty fish, consider discussing omega-3 supplements with your healthcare provider.
Plant sterols and stanols are compounds found in some fortified foods and supplements. They can block cholesterol absorption in the intestines, leading to reduced LDL cholesterol levels. Look for products that are fortified with these compounds, such as certain margarines and orange juice.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is another supplement that may offer cardiovascular benefits, particularly for individuals taking statin medications. It can help counteract some of the side effects of statins and support overall heart health.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements to ensure they are appropriate for your health needs.
Herbal Remedies and Their Benefits
Several herbal remedies have shown promise in aiding cholesterol management. Garlic, for instance, has been widely studied for its heart-health benefits. It may help lower cholesterol levels and reduce blood pressure.
Consuming fresh garlic or garlic supplements can be beneficial, though it’s important to discuss with your healthcare provider, especially if you are on medication.
Other herbs like turmeric and ginger possess anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit cardiovascular health.
Turmeric contains curcumin, which may help lower cholesterol levels and improve blood vessel function. Incorporating these herbs into your diet—whether through cooking, teas, or supplements—can support overall heart health.
Conclusion
Managing cholesterol levels is a vital aspect of maintaining heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. By making informed dietary choices, adopting healthier lifestyle habits, and considering natural remedies, you can significantly impact your cholesterol profile and overall well-being.
Incorporating heart-healthy foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants can help lower LDL cholesterol while promoting HDL cholesterol. Limiting saturated and trans fats, along with sugar and refined carbohydrates, is equally important. Regular physical activity not only helps manage cholesterol but also supports weight management and reduces stress, all of which contribute to a healthier heart.
Additionally, natural supplements and herbal remedies can provide supportive benefits, enhancing your efforts in cholesterol management. However, it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure these approaches align with your individual health needs.