Common Causes of Lower Back Pain in Women
Lower back pain is a widespread issue among women and can arise from a variety of sources. Understanding these causes can help in finding appropriate relief and treatment.
Muscle Strain and Ligament Sprain
Often, lower back pain begins with muscle strain or ligament sprain due to overexertion or sudden, awkward movements. This type of pain is usually a dull ache, accompanied by stiffness and occasional muscle spasms. Poor posture is another significant factor; sitting or standing incorrectly for long periods can place extra stress on the lower back, leading to persistent discomfort that generally improves with proper posture adjustments.
Spinal Disc Issues
Problems with the spinal discs are also a common cause of lower back pain. Discs can bulge or rupture, pressing on nearby nerves and causing sharp, shooting pain that may radiate down the legs, often accompanied by numbness or tingling. As individuals age, spinal discs naturally lose their cushioning, which can lead to chronic pain that typically worsens with activity and improves with rest.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, a condition where the cartilage in the spine deteriorates over time, can result in significant lower back pain and stiffness, particularly affecting the hips. This condition leads to discomfort that can become more pronounced with age and activity.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis, characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine, might cause noticeable changes in the shape of the back and result in discomfort. This condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including lower back pain.
Endometriosis
For some women, lower back pain is linked to endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. This often causes pelvic pain that can extend to the lower back, especially during menstruation.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), an infection in the reproductive organs, can also cause lower back pain. This infection leads to discomfort in the lower abdomen and back, and may be accompanied by symptoms like unusual discharge.
Pregnancy-Related Back Pain
Pregnancy can be a significant factor contributing to lower back pain. The additional weight and changes in posture during pregnancy place strain on the lower back, causing discomfort that usually improves after childbirth.
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual cycles can bring about lower back pain due to hormonal changes and uterine contractions. This type of pain often coincides with the menstrual period and can vary in intensity.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition marked by widespread pain, including in the lower back. It is often accompanied by fatigue and sleep disturbances, which can exacerbate the sensation of pain.
Kidney Issues
Issues with the kidneys, such as stones or infections, can lead to severe lower back pain. This pain might be accompanied by additional symptoms such as painful urination or blood in the urine.
Infections and Inflammatory Diseases
Infections or inflammatory diseases like osteomyelitis or ankylosing spondylitis can also cause lower back pain. These conditions often worsen with rest and may be accompanied by symptoms such as fever and weight loss.
Hormonal Influences and Lower Back Pain
Hormonal changes can significantly impact lower back pain in women. Fluctuations in hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can influence the body’s pain perception and muscle relaxation. For example, during the menstrual cycle, these hormonal shifts can lead to increased inflammation and sensitivity in the pelvic area, which can radiate to the lower back.
Similarly, hormonal changes during pregnancy cause ligaments to become more flexible in preparation for childbirth, often resulting in back pain. Addressing these hormonal influences involves managing symptoms through lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise, and consulting healthcare providers for tailored advice.
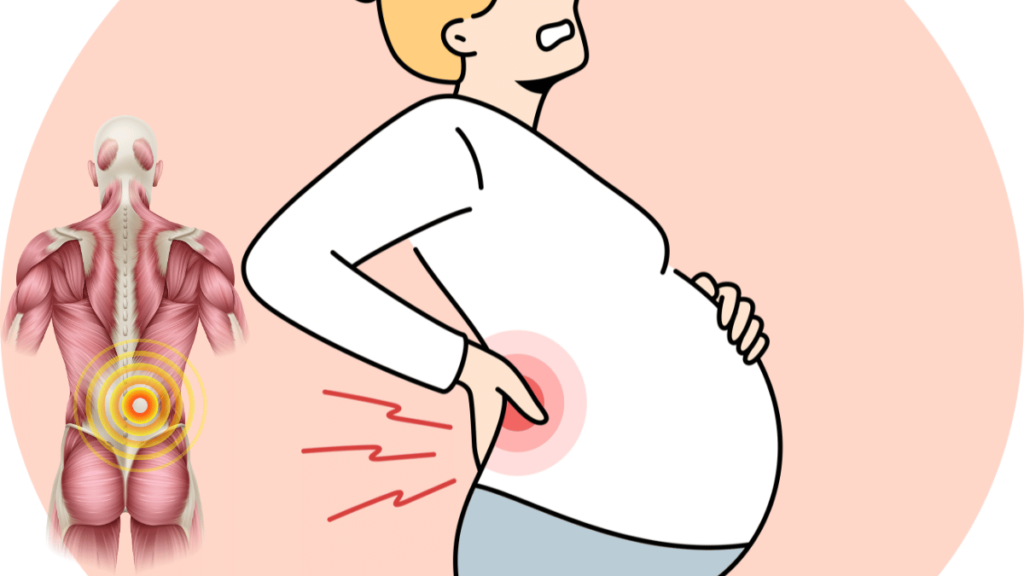
Pregnancy-Related Back Pain: Causes and Management
Pregnancy-related back pain is a widespread issue that many women face. As pregnancy progresses, the growing uterus shifts the body’s center of gravity, placing additional strain on the lower back. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy cause the ligaments in the pelvic region to loosen, increasing the risk of back pain.
To manage pregnancy-related back pain, women can benefit from maintaining proper posture, using supportive pillows, wearing comfortable and supportive shoes, and performing gentle stretches. Engaging in prenatal yoga or physical therapy can also provide relief. Consulting with a healthcare provider can offer further personalized strategies to alleviate pain.
Menstrual Cycle and Lower Back Pain: What You Need to Know
Lower back pain associated with the menstrual cycle is a common concern for many women. The hormonal fluctuations that occur during menstruation can lead to inflammation and increased sensitivity in the lower back. Menstrual cramps, which result from the uterus contracting to shed its lining, can also contribute to lower back pain. To alleviate menstrual-related back pain, women can use heat therapy, stay active, and consider over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen. Tracking your menstrual cycle and discussing pain management strategies with a healthcare provider can help address and reduce symptoms effectively.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Lower Back Pain in Women
Several lifestyle factors can exacerbate lower back pain in women. Prolonged sitting, poor posture, and a lack of physical activity often contribute to back discomfort. Carrying heavy bags, wearing unsupportive footwear, and maintaining an unhealthy weight can also put extra strain on the back. To prevent and manage lower back pain, it’s essential to adopt a healthy lifestyle.
This includes regular exercise to strengthen core muscles, maintaining good posture, using ergonomic furniture, and avoiding excessive strain. Making these adjustments can help reduce the risk of developing or worsening lower back pain.
Chronic Conditions Affecting Lower Back Pain in Females
Chronic conditions such as fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, and endometriosis can significantly affect lower back pain in women. Fibromyalgia causes widespread pain and tenderness throughout the body, including the lower back, often accompanied by fatigue and sleep issues.
Osteoarthritis leads to the breakdown of cartilage in the spine, resulting in pain and stiffness. Endometriosis involves tissue similar to the uterine lining growing outside the uterus, causing severe lower back pain, especially during menstruation. Managing these chronic conditions often requires a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications tailored to the specific condition.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Lower Back Pain

It’s crucial to seek medical advice for lower back pain when it is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs.
Consult a healthcare provider if the pain interferes with daily activities, follows a traumatic injury, or is associated with other health issues like fever or unexplained weight loss. Early intervention can help diagnose the underlying cause of the pain and provide appropriate treatment to prevent complications and improve overall quality of life.
Effective Treatments and Prevention Strategies for Lower Back Pain
Effective treatments for lower back pain depend on the underlying cause but generally include a combination of rest, physical therapy, and medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, while physical therapy focuses on strengthening muscles and improving flexibility.
Preventing lower back pain involves maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular exercise. Additionally, making ergonomic adjustments to your workspace and avoiding activities that strain the back are crucial for prevention. For persistent pain, consulting a healthcare provider for specialized treatments or interventions is recommended.
Summary
Lower back pain in women can stem from various sources, including muscle strain or ligament sprain from overuse or poor posture. Spinal disc issues, such as bulging or ruptured discs, can cause sharp pain and radiate to the legs. Osteoarthritis and scoliosis also contribute to back pain through cartilage deterioration and abnormal spine curvature, respectively. Conditions like endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) lead to discomfort in the lower back due to pelvic inflammation or infection. Pregnancy-related changes and menstrual cycles can exacerbate back pain through weight shifts and hormonal changes. Chronic conditions like fibromyalgia and kidney issues are additional factors. Effective management often involves addressing the underlying cause, maintaining good posture, and seeking medical advice for persistent pain.
FAQs
What are the most common causes of lower back pain in women?
Muscle strain, poor posture, spinal disc issues, osteoarthritis, scoliosis, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, pregnancy, menstrual cycles, fibromyalgia, and kidney problems.
How can muscle strain or ligament sprain lead to lower back pain?
It causes dull aches, stiffness, and spasms due to overuse or sudden movements.
What are spinal disc issues and how do they cause pain?
Bulging or ruptured discs press on nerves, causing sharp pain that can radiate down the legs.
How does osteoarthritis affect the lower back?
It deteriorates spinal cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness.
Can scoliosis cause lower back pain?
Yes, the abnormal curvature of the spine can lead to discomfort.


